Vitamin C is the only water-soluble vitamin that doesn’t belong to the vitamin B category. It is one of the body’s main antioxidants and is required for collagen synthesis.
*Milkymushrooms : 100g provides 12.82mg of vitamin C*
Types
Vitamin C comes in two forms, the most common of which is known as ascorbic acid.
An oxidized form of ascorbic acid called dehydroascorbic acid also has vitamin C activity.
Role and Function
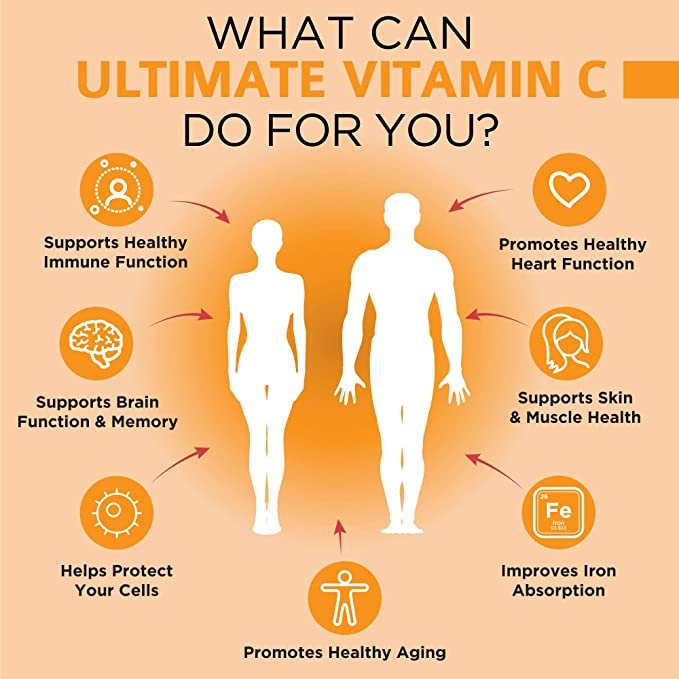
Vitamin C supports many essential body functions, including:
- Antioxidant defenses: Your body uses antioxidants to protect itself against oxidative stress. Vitamin C is one of its most important antioxidants.
- Collagen formation: Without vitamin C, the body is unable to synthesize collagen, the main protein in connective tissue. As a result, deficiency affects your skin, tendons, ligaments and bones.
- Immune function: Immune cells contain high levels of vitamin C. During an infection, its levels are quickly deplete.
Unlike the B vitamins, vitamin C doesn’t act as a coenzyme, although it is a cofactor for prolyl hydroxylase, an enzyme that serves an essential role in the formation of collagen
Vitamin C has many health benefits. For example, it helps strengthen our immune system and may help lower blood pressure. It is found in many fruits and vegetables.
Vitamin C is an essential vitamin, meaning your body can’t produce it. Yet, it has many roles and has been linked to impressive health benefits.
It’s water-soluble and found in many fruits and vegetables, including oranges, strawberries, kiwi fruit, bell peppers, broccoli, kale, and spinach.
The recommended daily intake for vitamin C is 75 mg for women and 90 mg for men.
While it’s commonly advised to get your vitamin C intake from foods, many people turn to supplements to meet their needs.
1. May reduce your risk of chronic disease
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that can strengthen your body’s natural defenses.
Antioxidants are molecules that boost the immune system. They do so by protecting cells from harmful molecules called free radicals.
When free radicals accumulate, they can promote a state known as oxidative stress, which has been linked to many chronic diseases.
Studies show that consuming more vitamin C can increase your blood antioxidant levels by up to 30%. This helps the body’s natural defenses fight inflammation.
SUMMARY
Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant that can boost your blood antioxidant levels. This may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease.
2. May help manage high blood pressure
Approximately one-third of American adults have high blood pressure (6).
High blood pressure puts you at risk of heart disease, the leading cause of death globally.
Studies have shown that vitamin C may help lower blood pressure in both those with and without high blood pressure.
An animal study found that taking a vitamin C supplement helped relax the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart, which helped reduce blood pressure levels.
Moreover, an analysis of 29 human studies found that taking a vitamin C supplement reduced systolic blood pressure (the upper value) by 3.8 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure (the lower value) by 1.5 mmHg, on average, in healthy adults.
In adults with high blood pressure, vitamin C supplements reduced systolic blood pressure by 4.9 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure by 1.7 mmHg, on average.
While these results are promising, it’s not clear whether the effects on blood pressure are long term. Moreover, people with high blood pressure should not rely on vitamin C alone for treatment.
SUMMARY
Vitamin C supplements have been found to lower blood pressure in both healthy adults and those with high blood pressure.
3. May lower your risk of heart disease
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide.
Many factors increase the risk of heart disease, including high blood pressure, high triglyceride or LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, and low levels of HDL (good) cholesterol.
Vitamin C may help reduce these risk factors, which may reduce heart disease risk.
For example, an analysis of 9 studies with a combined 293,172 participants found that after 10 years, people who took at least 700 mg of vitamin C daily had a 25% lower risk of heart disease than those who did not take a vitamin C supplement
Interestingly, another analysis of 15 studies found that consuming vitamin C from foods — not supplements — was linked to a lower risk of heart disease.
However, scientists were unsure whether people who consumed vitamin-C-rich foods also followed a healthier lifestyle than people who took a supplement. Thus, it remains unclear whether the differences were due to vitamin C or other aspects of their diet
Another analysis of 13 studies looked at the effects of taking at least 500 mg of vitamin C daily on risk factors for heart disease, such as blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
The analysis found that taking a vitamin C supplement significantly reduced LDL (bad) cholesterol by approximately 7.9 mg/dL and blood triglycerides by 20.1 mg/dL.
In short, it seems that taking or consuming at least 500 mg of vitamin C daily may reduce the risk of heart disease. However, if you already consume a vitamin-C-rich diet, then supplements may not provide additional heart health benefits.
SUMMARY
Vitamin C supplements have been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. These supplements may lower heart disease risk factors, including high blood levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides.
4. May reduce blood uric acid levels and help prevent gout attacks
GOUT is a type of arthritis that affects approximately 4% of American adults.
It’s incredibly painful and involves inflammation of the joints, especially those of the big toes. People with gout experience swelling and sudden, severe attacks of pain.
Gout symptoms appear when there is too much uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a waste product produced by the body. At high levels, it may crystallize and deposit in the joints.
Interestingly, several studies have shown that vitamin C may help reduce uric acid in the blood and, as a result, protect against gout attacks.
For example, a study including 1,387 men found that those who consumed the most vitamin C had significantly lower blood levels of uric acid than those who consumed the least
Another study followed 46,994 healthy men over 20 years to determine whether vitamin C intake was linked to developing gout. It found that people who took a vitamin C supplement had a 44% lower gout risk.
Additionally, an analysis of 13 studies found that taking a vitamin C supplement over 30 days significantly reduced blood uric acid, compared with a placebo.
While there appears to be a strong link between vitamin C intake and uric acid levels, more studies on the effects of vitamin C on gout are needed.
SUMMARY
Vitamin-C-rich foods and supplements have been linked to reduced blood uric acid levels and lower risk of gout.

5. Helps prevent iron deficiency
Iron is an important nutrient that has a variety of functions in the body. It’s essential for making red blood cells and transporting oxygen throughout the body.
Vitamin C supplements can help improve the absorption of iron from the diet. Vitamin C assists in converting iron that is poorly absorbed, such as plant-based sources of iron, into a form that is easier to absorb.
This is especially useful for people on a meat-free diet, as meat is a major source of iron.
In fact, simply consuming 100 mg of vitamin C may improve iron absorption by 67%.
As a result, vitamin C may help reduce the risk of anemia among people prone to iron deficiency.
In one study, 65 children with mild iron deficiency anemia were given a vitamin C supplement. Researchers found that the supplement alone helped control their anemina
If you have low iron levels, consuming more vitamin-C-rich foods or taking a vitamin C supplement may help improve your blood iron levels.
SUMMARY
Vitamin C can improve the absorption of iron that is poorly absorbed, such as iron from meat-free sources. It may also reduce the risk of iron deficiency.
6. Boosts immunity
One of the main reasons people take vitamin C supplements is to boost their immunity, as vitamin C is involved in many parts of the immune system.
First, vitamin C helps encourage the production of white blood cells known as lymphocytes and phagocytes, which help protect the body against infections .
Second, vitamin C helps these white blood cells function more effectively while protecting them from damage by potentially harmful molecules, such as free radicals.
Third, vitamin C is an essential part of the skin’s defense system. It’s actively transported to the skin, where it can act as an antioxidant and help strengthen the skin’s barriers.
Studies have also shown that taking vitamin C may shorten wound healing time.
What’s more, low vitamin C levels have been linked to poor health outcomes.
For example, people who have pneumonia tend to have lower vitamin C levels, and vitamin C supplements have been shown to shorten the recovery time.
SUMMARY
Vitamin C may boost immunity by helping white blood cells function more effectively, strengthening your skin’s defense system, and helping wounds heal faster
7. Protects your memory and thinking as you age
Dementia is a broad term used to describe symptoms of poor thinking and memory.
It affects over 35 million people worldwide and typically occurs among older adults.
Studies suggest that oxidative stress and inflammation near the brain, spine, and nerves (altogether known as the central nervous system) can increase the risk of dementia.
Vitamin C is a strong antioxidant. Low levels of this vitamin have been linked to an impaired ability to think and remember.
Moreover, several studies have shown that people with dementia may have lower blood levels of vitamin C .
Furthermore, high vitamin C intake from food or supplements has been shown to have a protective effect on thinking and memory as you age.
Vitamin C supplements may aid against conditions like dementia if you don’t get enough vitamin C from your diet. However, additional human studies are needed to understand the effects of vitamin C supplements on nervous system health.
SUMMARY
Low vitamin C levels have been linked to an increased risk of memory and thinking disorders like dementia, while a high intake of vitamin C from foods and supplements has been shown to have a protective effect.
Unproven claims about vitamin C
While vitamin C has many scientifically proven benefits, it also has many unfounded claims supported by either weak evidence or no evidence at all.
Here are some unproven claims about vitamin C:
- Prevents the common cold. While vitamin C appears to reduce the severity of colds and recovery time by 8% in adults and 14% in children, it does not prevent them.
- Reduces cancer risk. A handful of studies have linked vitamin C intake to a lower risk of several cancers. However, most studies have found that vitamin C does not affect the risk of developing cancer.
- Protects against eye disease. Vitamin C has been linked to reduced risks of eye diseases like cataracts and age-related macular degeneration. However, vitamin C supplements have no effect or may even cause harm.
- May treat lead toxicity. Although people with lead toxicity appear to have low vitamin C levels, there is no strong evidence from human studies that show vitamin C can treat lead toxicity.
SUMMARY
Although vitamin C has many proven benefits, it has not been shown to prevent the common cold, reduce cancer risk, protect against eye diseases, or treat lead toxicity.
Dietary Sources
The main dietary sources of vitamin C are fruits and vegetables.
Cooked animal-sourced foods contain virtually no vitamin C, but low amounts can be found in raw liver, eggs, fish roe, meat and fish
The chart below provides examples of some raw fruits and vegetables that are exceptionally rich in vitamin C.
Cooking or drying foods significantly reduces their vitamin C content.
Recommended Intake
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of vitamin C is the estimated amount of the vitamin most people need every day.
The table below also shows the tolerable upper limit (UL), which is the highest level of intake thought to be completely safe for most people.
No RDA has been established for infants. Instead, scientists have estimated their adequate intake, which is similar to the RDA, but based on weaker evidence.
| RDA (mg/day) | UL (mg/day) | ||
| Infants | 0–6 months | 40* | – |
| 7–12 months | 50* | – | |
| Children | 1–3 years | 15 | 400 |
| 4–8 years | 25 | 650 | |
| 9–13 years | 45 | 1,200 | |
| Women | 14–18 years | 65 | 1,800 |
| 19+ years | 75 | 2,000 | |
| Men | 14–18 years | 75 | 1,800 |
| 19+ years | 90 | 2,000 | |
| Pregnancy | 80–85 | 1,800–2,000 | |
| Lactation | 115–120 | 1,800–2,000 |
*Adequate intake
Deficiency
Deficiency is rare in Western countries, but may develop in people who follow restrictive diets or eat almost no fruits or vegetables. People with drug addiction or alcoholism are also at greater risk.
It leads to a disease known as scurvy, which is characterized by the breakdown of connective tissue .
The first symptoms of deficiency include fatigue and weakness. As scurvy becomes worse, people may experience spotted skin and inflamed gums.
Advanced scurvy may cause loss of teeth, bleeding gums and skin, joint problems, dry eyes, swelling and impaired wound healing. Like all vitamin deficiencies, scurvy is fatal without treatment.

Side Effects and Toxicity
Most people tolerate high doses of vitamin C without any side effects.
However, very high doses exceeding 3 grams per day cause diarrhea, nausea and abdominal cramps. This is because only a limited amount of vitamin C can be absorbed from a single dose.
Taking high-dose supplements over 1,000 mg per day may also increase the risk of kidney stones in predisposed people.
Benefits of Supplements
There is mixed evidence that vitamin C supplements benefit people who get adequate amounts from the diet.
However, vitamin C can improve iron absorption from a meal, helping those who are low or deficient in iron.
Additionally, one analysis of 29 studies concluded that supplements that provide at least 200 mg of vitamin C per day may help you recover from the common cold.
While vitamin C supplements may also help lower blood pressure, there is no evidence that they reduce the risk of heart disease.
Studies also suggest vitamin C may reduce the risk of cognitive decline, improve blood vessel function and reduce blood sugar levels, but high-quality studies are needed before definite conclusions can be reached.
Summary of Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that’s vital for the maintenance of connective tissue.
The main dietary sources are fruits and vegetables, but low amounts can be acquired from raw animal-sourced foods. Deficiency, known as scurvy, is rare in developed countries.
Most people tolerate high-dose supplements without any adverse effects. However, studies on the benefits of vitamin C supplements have had mixed results, suggesting supplements may not be that useful for those who already get sufficient amounts from their diets.
The Bottom Line
Most vitamins are water-soluble. These include the eight B vitamins as well as vitamin C.
Their roles in the body range widely, but most function as coenzymes in numerous metabolic pathways.
All the water-soluble vitamins are easy to get from a balanced diet. However, vitamin B12 is only found in substantial amounts in animal-sourced foods. As a result, vegans are at a high risk of deficiency and may need to take supplements or get regular injections.
Keep in mind that your body generally doesn’t store water-soluble vitamins, except for vitamin B12. Optimally, you should get them from your diet every day.
